
Table of Contents
- Significance of Self-assessment in GST
- Unveiling the Power of GST Returns: Compliance, Insights, and Effective Tax Administration
- Self-assessment Basis
- Supporting Sheet for Tax Authorities
- Impact on Tax Liability of Other Taxpayers
- Transfer of Information and Compliance Verification
- Inputs for Policy Decisions
- Management of Anti-evasion Programs
- Conclusion
Check out Taxmann X GSTPAM | GST Practical Guides | Introduction to GST Returns, Statements and Other Compliance Forms which provides insights into GST Returns, Statements and other Compliance Forms. This book will be helpful for tax practitioners and legal professionals. It is amended by the Finance Act 2023 and is developed by the Goods & Services Tax Practitioners' Association of Maharashtra.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) law, implemented in India on July 1, 2017, is a comprehensive tax reform that replaces various indirect taxes levied by the Central and State governments. It marks a significant milestone in India’s taxation system and aims to simplify and streamline the tax structure, promote ease of doing business, and create a unified market across the country.
The GST law is built on the principles of self-assessment, which require every registered person to assess and discharge their tax liability. Here is a detailed explanation of the key features and principles of the GST law:
- Scope of GST: The GST law applies to the supply of goods and services within India, including imports and certain specified activities. It is a destination-based tax, meaning that the tax is levied at the final point of consumption.
- Dual GST Structure: The GST system in India follows a dual structure, consisting of Central GST (CGST) and State GST (SGST). Both the Central and State governments have the authority to levy and administer the GST within their respective jurisdictions.
- Integrated GST (IGST): In addition to CGST and SGST, the GST law also provides for Integrated GST (IGST) on inter-state supplies of goods and services. IGST is collected by the Central government and then distributed to the respective States.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC): The GST law allows registered taxpayers to claim input tax credit, which is the credit of GST paid on inputs (purchases) that can be used to offset the GST liability on output (sales). This helps in eliminating cascading or double taxation and encourages the free flow of credits across the supply chain.
- Composition Scheme: Small businesses with a turnover below a specified threshold have the option to avail the composition scheme. Under this scheme, taxpayers can pay GST at a fixed percentage of their turnover and are relieved from detailed compliance procedures.
- Electronic Filing and Compliance: The GST law emphasizes electronic filing and compliance. Taxpayers are required to register, maintain records, and file returns online through the GST portal. Various compliances, such as filing monthly/quarterly returns, payment of taxes, and reconciliation, are conducted electronically.
- GST Council: The GST law established the GST Council, a constitutional body comprising representatives from the central and state governments. The GST Council is responsible for making recommendations on important aspects of the GST, including tax rates, exemptions, and procedural changes.
- Anti-Profiteering Measures: The GST law includes anti-profiteering provisions to ensure that the benefits of GST rate reductions or input tax credit are passed on to the end consumers. Businesses are required to maintain transparency in their pricing and comply with anti-profiteering regulations.
- Dispute Resolution: The GST law provides for a mechanism to resolve disputes through various appellate authorities, including the Appellate Authority for Advance Ruling, the GST Appellate Tribunal, and the High Court or Supreme Court.
- GST Network (GSTN): The GSTN is a technological backbone that supports the implementation of the GST law. It serves as a common IT platform for registration, return filing, payment processing, and other GST-related processes.
Overall, the GST law in India aims to create a simplified and transparent tax regime by unifying multiple taxes, eliminating cascading effects, promoting ease of compliance, and fostering a common market across States. It represents a significant shift in the country’s taxation system and has had a substantial impact on businesses and taxpayers across various sectors.
1. Significance of Self-assessment in GST
Section 59 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017, plays a crucial role in the Indian taxation system. It imposes an obligation on every registered person to carry out self-assessment of their tax dues under the Act. Self-assessment refers to the process in which taxpayers calculate the amount of tax they owe and subsequently report this information to the tax authorities through the filing of periodic tax returns.
To ensure proper compliance with the self-assessment provisions, registered persons are required to furnish the prescribed tax returns & statements with accurate particulars in accordance with the CGST Act and CGST Rules. This means that taxpayers must carefully calculate their tax liabilities, taking into account various factors such as the applicable tax rates, input tax credits, and exemptions, among others. The accuracy of the information provided in the returns is crucial to maintain the integrity and transparency of the tax system.
By adhering to the self-assessment requirements, taxpayers contribute to the effective functioning of the GST (Goods and Services Tax) regime. It allows tax authorities to assess and verify the tax liabilities of registered persons, ensuring that the correct amount of tax is paid to the government. Self-assessment also helps in preventing tax evasion and maintaining a level playing field for businesses by ensuring that all registered persons are treated equally under the law.
In summary, section 59 of the CGST Act, 2017, emphasizes the importance of self-assessment for taxpayers. By accurately assessing and reporting their tax dues through periodic tax returns, registered persons fulfil their obligations and contribute to the smooth operation of the GST system in India.
2. Unveiling the Power of GST Returns: Compliance, Insights, and Effective Tax Administration
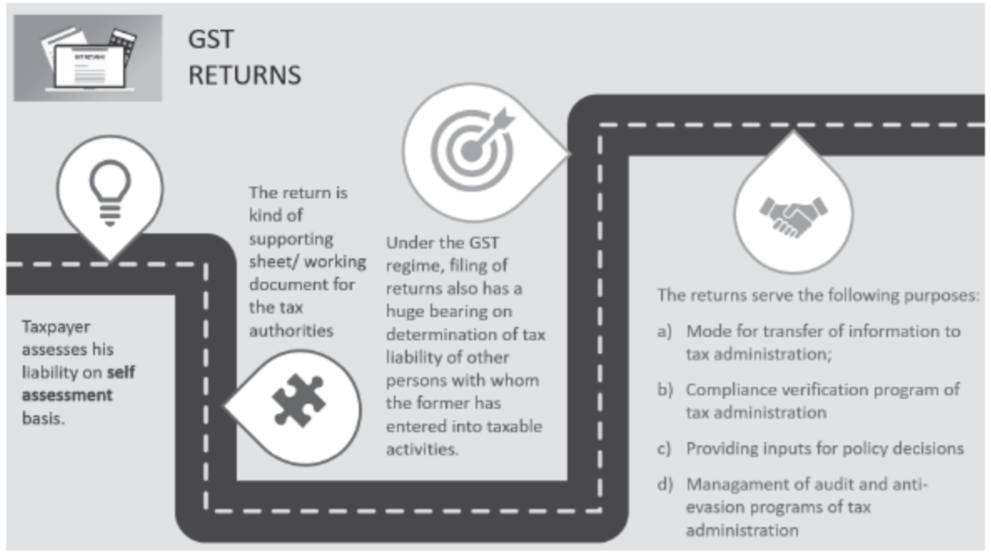
In the complex realm of Goods and Services Tax (GST), the filing of GST returns holds immense significance. This chapter delves into the crucial role played by GST returns as a self-assessment tool, supporting sheet for tax authorities, and as a powerful instrument influencing the tax liability of other taxpayers. Additionally, it highlights the significance of GST returns in facilitating the transfer of information to tax administration, enabling compliance verification programs, aiding policy decisions, and enhancing the effectiveness of anti-evasion measures.
3. Self-assessment Basis
GST returns serve as a vital means for registered taxpayers to self-assess their tax liabilities accurately. Through meticulous calculation and reporting of their tax dues, taxpayers fulfil their obligations and contribute to the efficient functioning of the GST system. This self-assessment basis promotes transparency and fairness, allowing taxpayers to review the tax implications of the business operations for the tax period and provide them with an opportunity to make their own tax calculations.
4. Supporting Sheet for Tax Authorities
GST returns act as comprehensive working documents that provide essential information to tax authorities. These returns furnish a detailed breakdown of sales, purchases, input tax credits, and other relevant financial data. This data not only aids tax administrators in cross-verification but also assists them in conducting audits, investigations, and assessments of tax liabilities. GST returns are indispensable tools in promoting transparency, accountability, and effective tax administration.
5. Impact on Tax Liability of Other Taxpayers
The accuracy and completeness of GST returns have a substantial bearing on the tax liabilities of other taxpayers. The information provided in these returns forms the basis for matching input tax credits, preventing fraudulent claims, and ensuring a level playing field among taxpayers. Timely and accurate filing of GST returns helps to maintain integrity within the tax system, minimizing the risk of undue burden or unfair advantages for compliant taxpayers.
6. Transfer of Information and Compliance Verification
GST returns facilitate the seamless transfer of information from taxpayers to the tax administration. This enables tax authorities to access and analyze data efficiently, conduct compliance verification programs, and identify potential cases of non-compliance. Through careful scrutiny of GST returns, tax authorities can detect discrepancies, assess compliance levels, and take appropriate enforcement actions.
7. Inputs for Policy Decisions
GST returns provide invaluable insights and data that support evidence-based policy decisions. The comprehensive information gathered from these returns aids in understanding economic trends, consumption patterns, and tax revenue projections. Such data empowers policymakers to design and implement effective tax policies, streamline compliance processes, and foster economic growth.
8. Management of Anti-evasion Programs
GST returns play a vital role in managing anti-evasion programs and combating tax evasion. The information provided in these returns helps tax authorities identify suspicious transactions, analyze patterns of non-compliance, and target enforcement actions accordingly. Effective utilization of GST returns strengthens the overall anti-evasion framework, ensuring the integrity and fairness of the tax system.
9. Conclusion
GST returns serve as the backbone of compliance in the GST regime, playing a pivotal role in self-assessment, supporting tax authorities, influencing tax liabilities, transferring information, verifying compliance, aiding policy decisions, and managing anti-evasion efforts. Understanding the significance and intricacies of GST returns is crucial for taxpayers, tax professionals, and policymakers alike, as they navigate the complexities of the GST landscape.
The post The Crucial Role of GST Returns in India’s Tax System appeared first on Taxmann Blog.



